Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) affects blood flow in the legs, causing both discomfort and visible changes. While the condition can develop gradually, understanding its signs helps with early recognition. Symptoms often vary, and knowing what to look for can guide discussions with a healthcare provider. Here are a few of the most frequently asked questions about chronic venous insufficiency:
Defining CVI
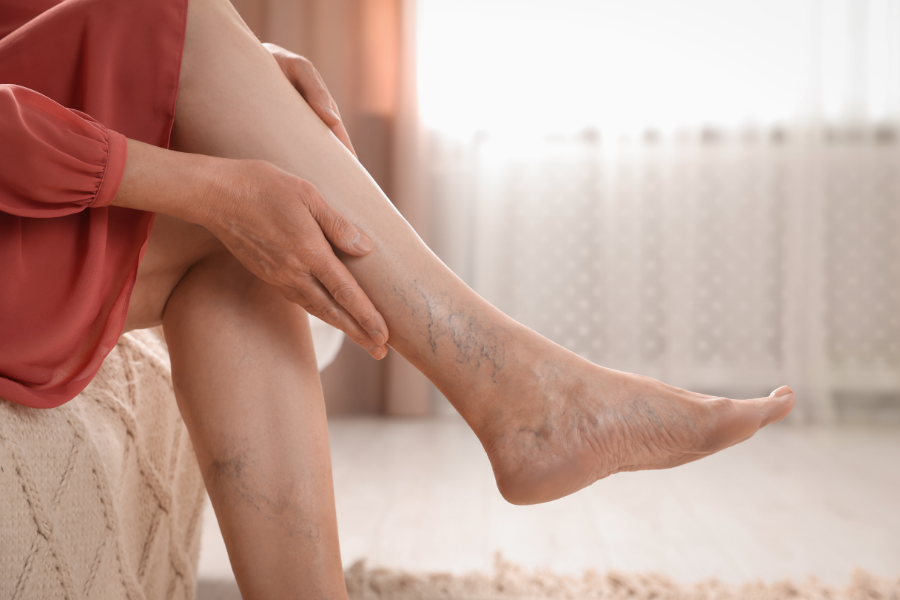
Chronic Venous Insufficiency occurs when veins in the legs struggle to return blood to the heart. Damaged valves can allow blood to flow backward, leading to pooling in the lower leg veins. This impaired circulation can contribute to discomfort and other visible changes over time.
People with CVI often notice symptoms primarily in their legs. Swelling, aching, or a heavy sensation are common, and some develop varicose veins, which are enlarged and twisted veins visible under the skin. Over time, skin in the affected areas may change in color or texture, reflecting underlying circulation issues.
Identifying Risk
Several factors may increase the likelihood of developing CVI. Genetics can play a role, and certain lifestyle habits or health conditions can further elevate risk. Being aware of these factors helps people understand why some individuals are more prone to vein issues than others. Common risk factors include:
- Being overweight or obese which puts extra pressure on the leg veins
- Pregnancy often affect circulation and vascular function
- A history of blood clots, such as DVT, that may damage the veins
- Smoking, which may weaken vein walls and impair circulation
- Prolonged periods of sitting or standing limit blood flow in the legs
Recognizing these risk factors can help individuals monitor their leg health, make lifestyle adjustments, and discuss preventive strategies with a healthcare provider.
Diagnosing CVI
Diagnosing CVI usually begins with a physical examination of the legs. Providers check for swelling, varicose veins, and skin discoloration. They also assess changes in texture and symptoms, such as heaviness or aching.
Ultrasound is a common imaging test used to evaluate blood flow and vascular function. This non-invasive procedure visualizes vein structure and identifies blockages or valve issues. Results help determine the severity of CVI and guide treatment decisions.
Available Treatments
Treatment for CVI focuses on improving blood flow and effectively managing symptoms. Conservative approaches often include wearing compression stockings, which support vein function and encourage blood flow upward. Elevating the legs periodically can help reduce swelling and relieve discomfort, especially after long periods of standing or sitting.
For more advanced cases, minimally invasive procedures may treat damaged veins directly. These treatments target affected veins while preserving surrounding tissue and reducing recovery time. Combining conservative care with procedural options can help manage symptoms and improve overall leg comfort and mobility.
Manage Chronic Venous Insufficiency Today
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can support vein health and overall leg circulation. Regular exercise, such as walking, helps keep blood flowing efficiently through the veins. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the leg veins, while avoiding long periods of inactivity also benefits circulation. Discover simple steps to support your vein health.