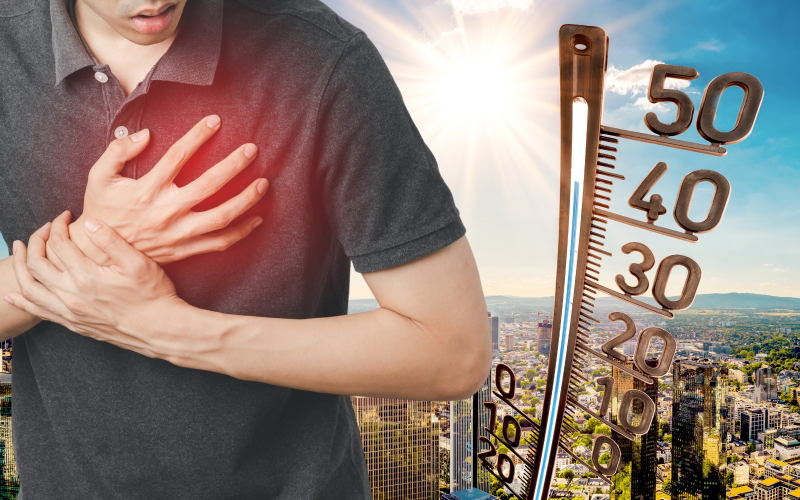
Cardiology addresses the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases and abnormalities. When temperatures rise, the body’s systems must adapt, and this adjustment may place specific demands on the heart. Here is more information on how hot weather interacts with cardiovascular health:
Increased Strain
High temperatures can impact various heart functions. To maintain a stable internal temperature, blood vessels may widen to release heat, a process known as vasodilation. The heart then needs to pump more blood to the skin’s surface. This response increases the heart’s workload, causing it to beat faster and circulate more blood per minute.
For individuals with healthy hearts, this added strain is usually manageable through cardiology. But for those with pre-existing heart conditions, the increased demand might be more than their heart are prepared to handle. The body’s cooling mechanism requires a significant amount of effort from the cardiovascular system, and this effort intensifies as the external temperature climbs.
Added Dehydration
Sweating is the body’s primary way to cool down, yet it leads to fluid loss. When these fluids are not replaced, dehydration may occur. Dehydration may reduce the volume of blood circulating in your body. This causes the heart to pump even faster and harder, making it difficult to deliver enough oxygen-rich blood to your muscles and organs.
A lower blood volume also may make the blood thicker. This change may elevate the risk of blood clots forming. For anyone, particularly those with a history of heart issues, staying hydrated is a straightforward way to support the heart’s function in hot weather. Drinking water regularly throughout the day helps maintain blood volume, allowing the heart to work more efficiently.
Worsened Conditions
Hot and humid weather can exacerbate symptoms for individuals with certain heart conditions. Individuals with congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, or high blood pressure might find that their symptoms become more pronounced in the heat. For instance, shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain might increase because the heart is already working overtime to cool the body.
The added stress from the heat, combined with potential dehydration, may create a challenging environment for a compromised heart. Air quality typically worsens on hot days, with higher levels of ozone and other pollutants. These pollutants may put additional stress on the cardiovascular system, compounding the effects of the heat itself.
Exacerbated Side Effects
Some medications used to treat heart conditions may affect the body’s response to heat. Other drugs, such as ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), may also affect the body’s response to heat. It is a good practice to be aware of how your prescribed medications interact with high temperatures. Understanding these interactions helps in managing your health during a heatwave.
Find Cardiology Services Near You
Managing your heart health is a year-round activity, and understanding environmental factors, such as heat, is part of that process. If you have questions about how hot weather affects your heart or need to speak with a specialist about your cardiovascular health, support is available. Contact a clinic to schedule a consultation with one of our cardiologists and get the guidance you need.