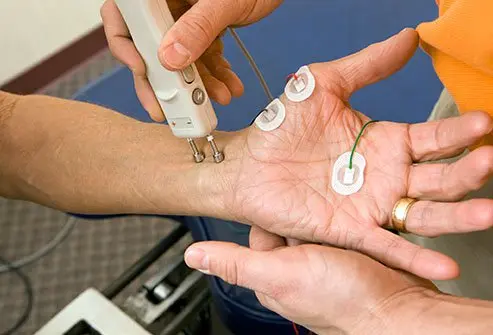
Neuropathy refers to a condition resulting from damaged or dysfunctional nerves, which can disrupt communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. Understanding this condition is a key aspect of neurology, as it involves the intricate workings of the peripheral nervous system. This system transmits signals that control everything from muscle movement to sensory information like touch and temperature. When these nerves are compromised, it can lead to a wide range of symptoms that affect daily life.
What Is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy describes a collection of disorders that occur when nerves of the peripheral nervous system are damaged. This system includes all the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. These nerves have specific functions, and damage can interfere with the signals they carry. This disruption may cause issues with sensory, motor, or autonomic functions.
The study and treatment of nerve-related conditions fall under the umbrella of neurology. A specialist in this field can help identify the underlying cause of nerve damage. Causes range from physical injury and infections to metabolic problems and exposure to toxins. Identifying the source is a primary step in developing a management plan.
How Many Types Exist?
Neuropathy is generally classified based on the number of nerves affected and the type of nerve cells that are damaged. This classification helps healthcare providers pinpoint the nature of the condition and tailor their approach to addressing it. Each type presents a unique set of challenges and symptoms for an individual.
There are over 100 types of neuropathy, but they can be grouped into several main categories:
- Mononeuropathy: This type affects a single nerve. A common form is carpal tunnel syndrome, which involves compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
- Multiple Mononeuropathy: This condition involves damage to two or more separate nerves in different areas of the body.
- Polyneuropathy: This is the most common type, affecting multiple nerves throughout the body, often symmetrically on both sides. It frequently begins in the feet and hands.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: This type impacts the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions. It can affect heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bladder function.
Knowing the classification helps your provider understand the extent of the nerve damage. A clear diagnosis is the foundation for managing the condition effectively.
What Are the Early Warning Signs?
Recognizing the early signs of neuropathy may prompt you to seek guidance sooner. Symptoms often develop gradually and can vary depending on which nerves are affected. Paying attention to new or unusual sensations in your body can be helpful. Some common early warning signs include:
- Numbness or Tingling: A pins-and-needles sensation, often starting in the hands or feet, that may spread upward into the legs or arms.
- Sharp or Burning Pain: Spontaneous pains that may feel jabbing, throbbing, or like an electric shock.
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty with coordination, muscle weakness, or even paralysis if motor nerves are affected. This may lead to stumbling or difficulty gripping objects.
- Sensitivity to Touch: Some people experience extreme sensitivity, where even light touch can cause significant pain.
Experiencing any of these signs does not automatically mean you have neuropathy, but they do warrant a conversation with a healthcare professional.
Consult a Neurology Provider
If you are experiencing symptoms consistent with neuropathy, discussing them with a provider is a practical next step. A professional in the field of neurology can perform a thorough evaluation to understand your specific situation. They can review your health history and conduct tests to assess your nerve function. Seeking a professional opinion can provide you with clarity and a path forward for managing your health.