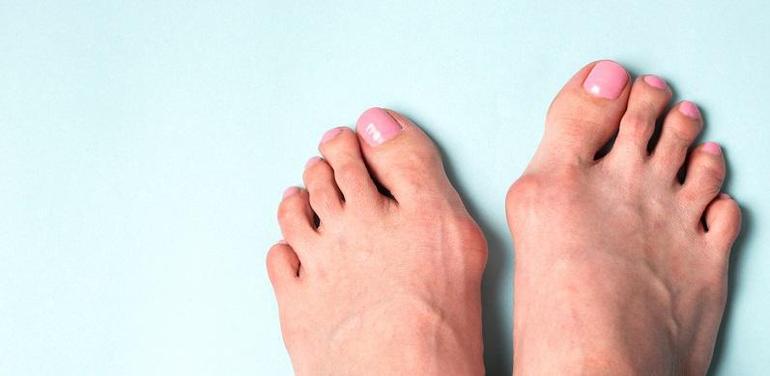
A bunion is a common foot deformity that develops at the base of the big toe. This condition causes the big toe to angle inward, toward the other toes, creating a bony bump on the joint’s outer edge. While often viewed as a cosmetic issue, a bunion is a progressive structural deformity that can lead to significant discomfort, pain, and difficulty with daily activities. Understanding the signs, causes, and available management strategies is a first step toward addressing the condition and maintaining foot health.
Recognize Early Bunion Signs
Early detection of a bunion is key to managing its progression. The most noticeable sign is a firm bump on the outside of the big toe joint, often accompanied by the big toe leaning toward the second toe. Symptoms such as redness, swelling, and tenderness around the joint can worsen with tight-fitting shoes. Some individuals may also experience stiffness or pain, accompanied by limited movement in the big toe.
Understand Common Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of bunions. These elements can increase an individual’s susceptibility to this foot condition. A combination of inherited traits, external pressures, and personal habits often plays a role.
- Genetic Predisposition: Inherited foot types (e.g., low arches, flat feet) can increase the likelihood of bunions, especially if they run in the family.
- Footwear Choices: Tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes place pressure on the big toe joint, leading to misalignment over time.
- Lifestyle and Activities: Jobs or activities involving prolonged standing/walking, as well as conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, can contribute to bunion formation.
Explore Effective Treatment Options
The approach to managing bunions often depends on the severity of the symptoms and the degree of deformity. The primary goals are to alleviate pressure, reduce pain, and slow the progression of the bump. For many, non-surgical methods are sufficient to manage discomfort. Treatment options may include:
- Changes in Footwear: Selecting shoes with a wide toe box, low heels, and supportive soles can relieve pressure on the joint.
- Padding and Taping: Using over-the-counter bunion pads can cushion the area, while taping the foot can help maintain proper alignment.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom or off-the-shelf shoe inserts can help control abnormal foot mechanics and support the joint.
- Pain Management: Applying ice packs can help reduce swelling and discomfort after periods of activity.
Prevent Bunion Progression
While complete bunion prevention isn’t always possible, especially when there is a genetic link, you can take steps to slow its progression and manage symptoms. The most effective strategy involves proper footwear that avoids constricting toes or pressuring joints. Regularly performing gentle foot and toe stretches can help maintain joint flexibility and mobility. Maintaining a healthy weight also reduces the overall stress placed on your feet with every step you take.
Choose Relief from Bunions
Recognizing the early signs of a bunion and understanding its contributing factors are beneficial for effective management. Treatments and preventive strategies can alleviate pain and slow the progression. Addressing the condition early offers more management options and helps preserve mobility. If you are experiencing persistent foot pain or notice changes in the structure of your foot, consult a professional.